# Title
Virtual Cell Challenge:
Toward a Turing test for the virtual cell
# Introduction
These
‘‘virtual cells’’ are expected to learn the
relationship between cell state and function
and are intended to predict the conse
quences of perturbations—such as a
gene knockdown or the application of a
drug—across cell types and cell contexts.
模型需要考虑到的因素:These models must account for
additional complexity—such as the cell
type, genetic background, and context of
a cell—as well as the cellular phenotype
being measured and predicted.
# Open-source competitions can lead to rapid progress
遇到的问题:Without standard
ized benchmarks and purpose-built
evaluation datasets that evolve in real
time alongside developments in the field,
it is difficult to evaluate whether models
are capturing generalizable biological
structure rather than dataset-specific
patterns.
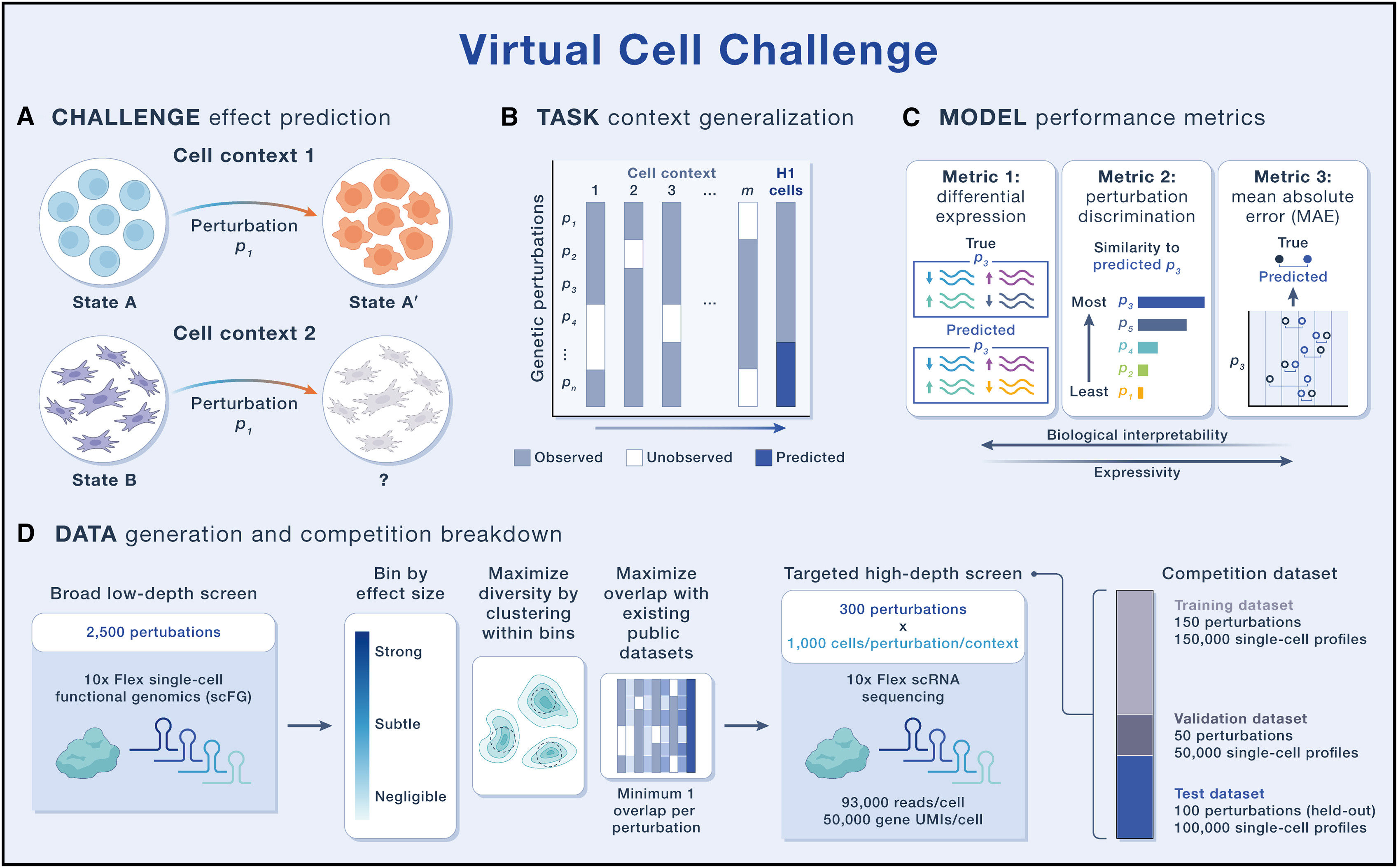
# Datasets
human embryonic stem cell line (H1 hESC)
scFG to
generate approximately 300,000 single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) profiles by silencing 300 carefully selected genes using CRISPR interference (CRISPRi)
# Format of the Virtual Cell Challenge Task
Predictive models can be trained to generalize along several axes.
- (1) generalization across biological context (e.g., cell type, cell line, culture conditions, or even in vivo versus in vitro settings)
- (2) generalization to novel genetic and/or chemical perturbations, including their combinations.
这里采用的形式是针对 cell type 进行预测,考虑到 zero-shot 的不切实际,采取 few-shot 作为训练模型的手段
# Evaluations
Evaluation metrics should reflect the core purpose of a virtual cell: simulating cellular behavior via in silico experiments—specifically, predicting gene expression responses to genetic perturbations.
- The differential expression score evaluates how accurately a model predicts differential gene expression, a key output of most scFG exoeriments and an essential input for downstream biological interpretation.
- The perturbation discrimination score
measures a model’s ability to distinguish
between perturbations by ranking predic
tions according to their similarity to the
true perturbational effect, regardless of
their effect size.
模型可能投机取巧:
- 如果只会输出固定的基因集 → DE 得分高,但扰动区分能力差。
- 如果只会在 embedding 空间里分组 → 扰动区分能力强,但 DE 无生物学意义。
mean absolute
error (MAE). While MAE is less biologically
interpretable, it captures overall predic
tive accuracy and provides a global view
of model performance across the entire
gene expression profile.